|
IRINOTECAN HYDROCHLORIDE |
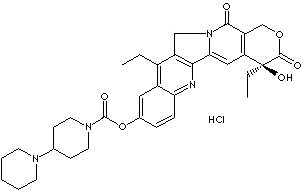
| Synonyms. Irinotecan hydrochloride; 7-Ethyl-10-(4-(1-piperidino)-1-piperidino)carbonyloxy camptothecin hydrochloride; CPT-11; Campto; Camptosar; Camptothecin 11 hydrochloride; Topotecin; (1,4'-Bipiperidine)-1'-carboxylic acid (S)-4,11-diethyl-3,4,12,14- tetrahydro- 4-hydroxy-3,14- dioxo-1Hpyrano (3',4':6,7)indolizino(1,2-b] quinolin-9-y) ester; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION | |
|
CAS RN |
100286-90-6, 136572-09-3 (Hydrate) |
|
EINECS RN |
213-584-9 |
|
FORMULA |
C33H38N4O6·HCl |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
623.14 |
|
H.S CODE |
2934.99.3000 |
|
SMILES |
C1(OCc2c([C@]1(CC)O)cc1c3c(Cn1c2=O)c(c1c(ccc(c1)OC(=O)N1CCC (CC1) N1CCCCC1)n3)CC)=O.Cl |
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Antineoplastic, Topoisomerase Inhibitor, Antitumor alkaloid |
|
EXTRA NOTES |
Irinotecan (Camptosar, Pfizer; Campto, Yakult Honsha) is a drug used for the treatment of cancer. Irinotecan prevents DNA from unwinding by inhibition of topoisomerase 1. In chemical terms, it is a semisynthetic analogue of the natural alkaloid camptothecin. http://en.wikipedia.org/ |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
|
PHYSICAL STATE. |
yellow crystalline powder |
|
MELTING POINT |
|
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
Slightly soluble |
| SOLVENT SOLUBILITY | Sparingly soluble in methanol |
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
log P(octanol-water) |
|
|
VAPOR PRESSURE |
|
|
AUTOIGNITION TEMP |
|
| pH |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions. |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Strong acids, Strong bases |
| POLYMERIZATION |
Has not been reported |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 1,Flammability:0, Reactivity: 0 |
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Camptothecin derivatives are clinically used antitumor alkaloids that belong to monoterpenoid indole alkaloids. In this study, we investigated the biosynthetic pathway of camptothecin from [1-13C]glucose (Glc) by in silico and in vivo studies. The in silico study measured the incorporation of Glc into alkaloids using the Atomic Reconstruction of Metabolism software and predicted the labeling patterns of successive metabolites from [1-13C]Glc. The in vivo study followed incorporation of [1-13C]Glc into camptothecin with hairy roots of Ophiorrhiza pumila by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. The 13C-labeling pattern of camptothecin isolated from the hairy roots clearly showed that the monoterpene-secologanin moiety was synthesized via the 2C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate pathway, not via the mevalonate pathway. This conclusion was supported by differential inhibition of camptothecin accumulation by the pathway-specific inhibitors (fosmidomycin and lovastatin). The quinoline moiety from tryptophan was also labeled as predicted by the Atomic Reconstruction of Metabolism program via the shikimate pathway. These results indicate that camptothecin is formed by the combination of the 2C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate pathway and the shikimate pathway. This study provides the innovative example for how a computer-aided comprehensive metabolic analysis will refine the experimental design to obtain more precise biological information. (http://www.plantphysiol.org/) Irinotecan hydrochloride: The hydrochloride salt of a semisynthetic derivative of camptothecin, a cytotoxic, quinoline-based alkaloid extracted from the Asian tree Camptotheca acuminata. Irinotecan, a prodrug, is converted to a biologically active metabolite 7-ethyl-10-hydroxy-camptothecin (SN-38) by a carboxylesterase-converting enzyme. One thousand-fold more potent than its parent compound irinotecan, SN-38 inhibits topoisomerase I activity by stabilizing the cleavable complex between topoisomerase I and DNA, resulting in DNA breaks that inhibit DNA replication and trigger apoptotic cell death. Because ongoing DNA synthesis is necessary for irinotecan to exert its cytotoxic effects, it is classified as an S-phase-specific agent. Check for active clinical trials or closed clinical trials using this agent. (NCI Thesaurus) (http://www.cancer.gov/) Irinotecan inhibits topoisomerase I, a DNA unwinding enzyme essential for cell division, resulting in inhibition of replication and breaks in single-strand DNA. In the UK, irinotecan is indicated for the treatment of patients with advanced colorectal cancer in combination with 5-FU/FA in patients without prior chemotherapy for advanced disease, and as a single agent in patients who have failed an established 5-FU-containing treatment regimen. It is associated with acute cholinergic symptoms, severe late-onset diarrhoea, myelosuppression and alopecia. Contraindications for irinotecan include chronic inflammatory bowel disease and bowel obstruction, bilirubin more than three times the upper limit of the normal range, WHO performance status more than 2, and severe bone marrow failure. (http://www.nice.org.uk/) Quinolones are a key group of antibiotics that interfere with DNA synthesis by inhibiting topoisomerase, most frequently topoisomerase II (DNA gyrase), an enzyme involved in DNA replication. DNA gyrase relaxes supercoiled DNA molecules and initiates transient breakages and rejoins phosphodiester bonds in superhelical turns of closed-circular DNA. This allows the DNA strand to be replicated by DNA or RNA polymerases. The fluoroquinolones, second-generation quinolones that include levofloxacin, norfloxacin, and ciprofloxacin, are active against both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Topoisomerases are present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, but the quinolones are specific inhibitors of bacterial topoisomerase II. Inhibitors that are effective against mammalian topoisomerases, such as irinotecan and etoposide, are used as antineoplastic drugs to kill cancer cells. (http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/)
|
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
yellowish crystalline powder |
|
IDENTIFICATION |
positive (Test A,B,C) |
| ASSAY | 98.0~102.0% (on dry basis) |
|
WATER CONTENT |
7.0 ~ 9.0% |
| SPECIFIC ROTATION | +60.0° ~ +72.0° |
|
RELATED SUBSTANCES |
1.0% max (total impurity) |
| pH |
3.0 ~ 5.0 |
| HEAVY METALS | 20ppm max |
| MICROBIOLOGICAL TEST |
Endotoxins 0.556IU/mg max |
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION | |
|
UN NO. |
Not regulated |
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| PACKING GROUP | |
|
|
| SAFETY INFORMATION |
|
|
HAZARD OVERVIEW |
OSHA Hazards; Target Organ Effect, Harmful by ingestion., Teratogen. Target Organs:Liver, Blood, Spleen., Bone marrow, Thymus. Harmful if swallowed. |
|
GHS |
|
|
SIGNAL WORD |
Warning |
|
PICTOGRAMS |
|
|
HAZARD STATEMENTS |
H302 |
|
P STATEMENTS |
|
| EC DIRECTIVES |
|
| HAZARD CODES |
|
|
RISK PHRASES |
22 |
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
|
|
|
| PACKING |
|
|